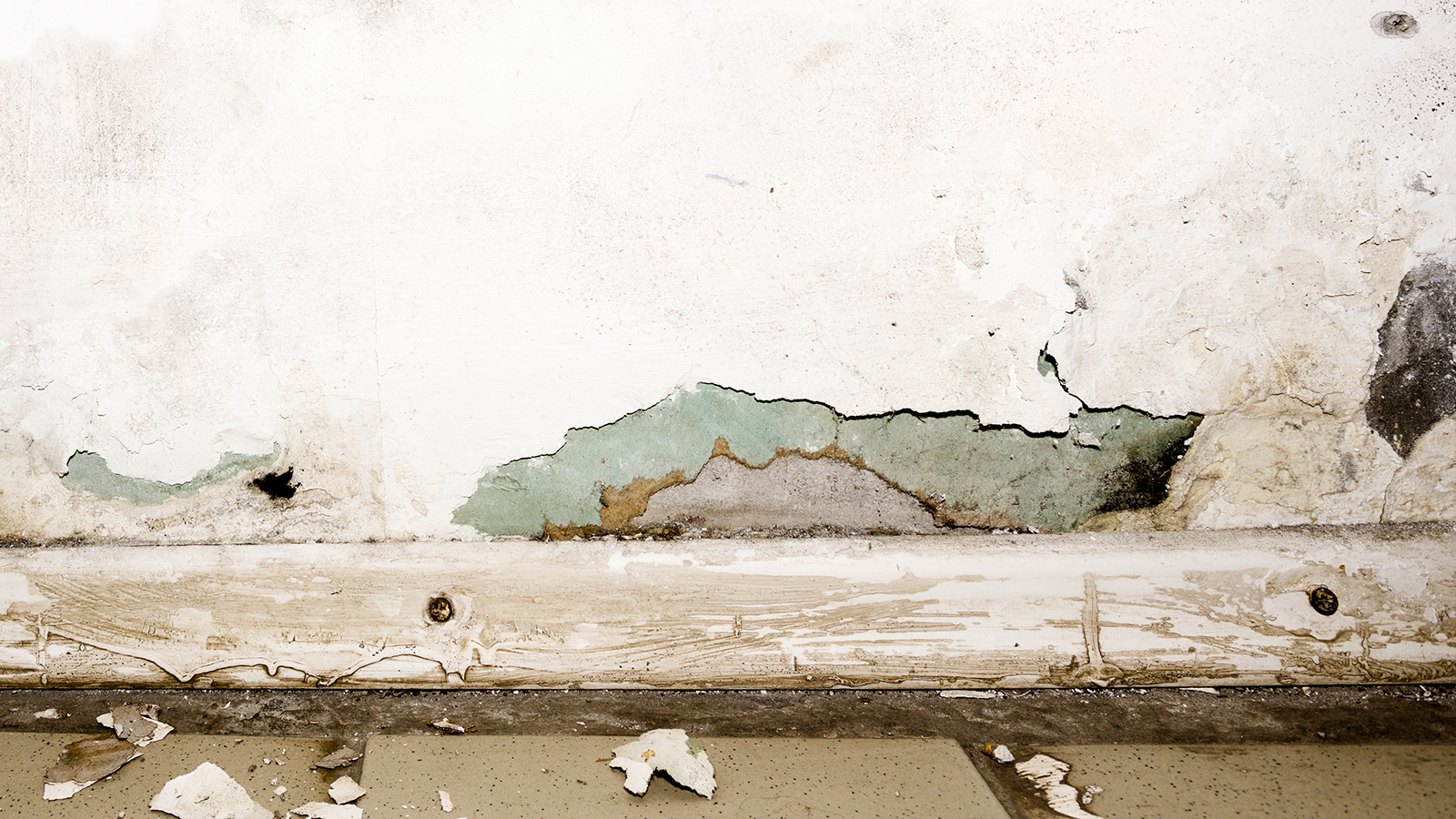
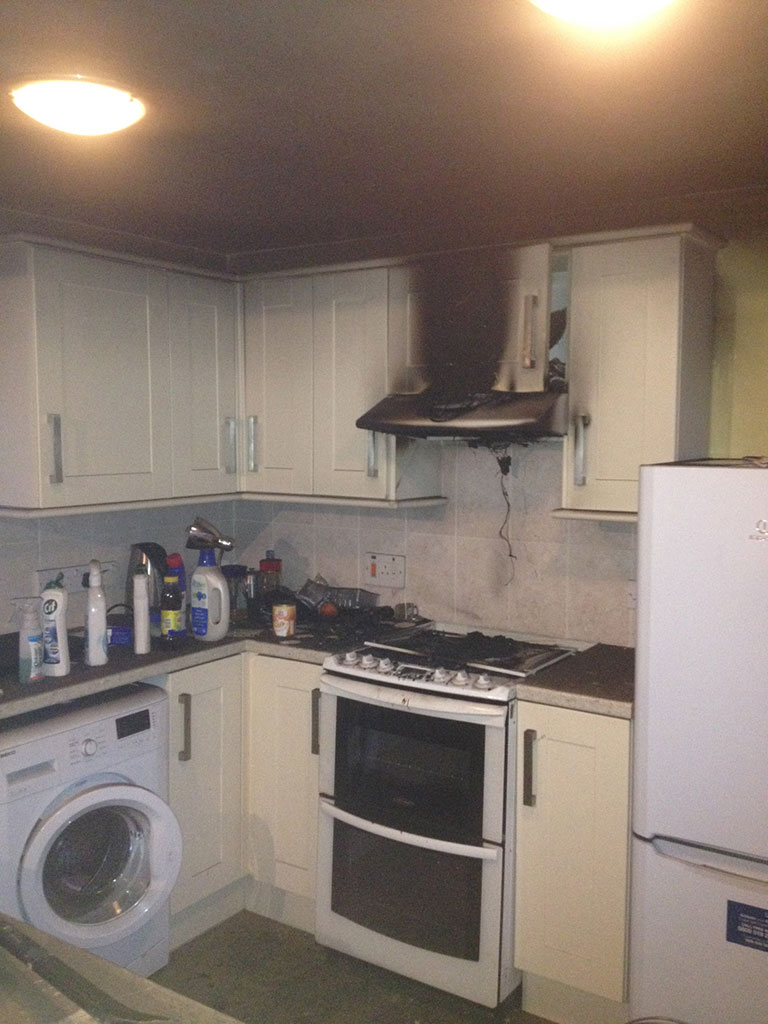
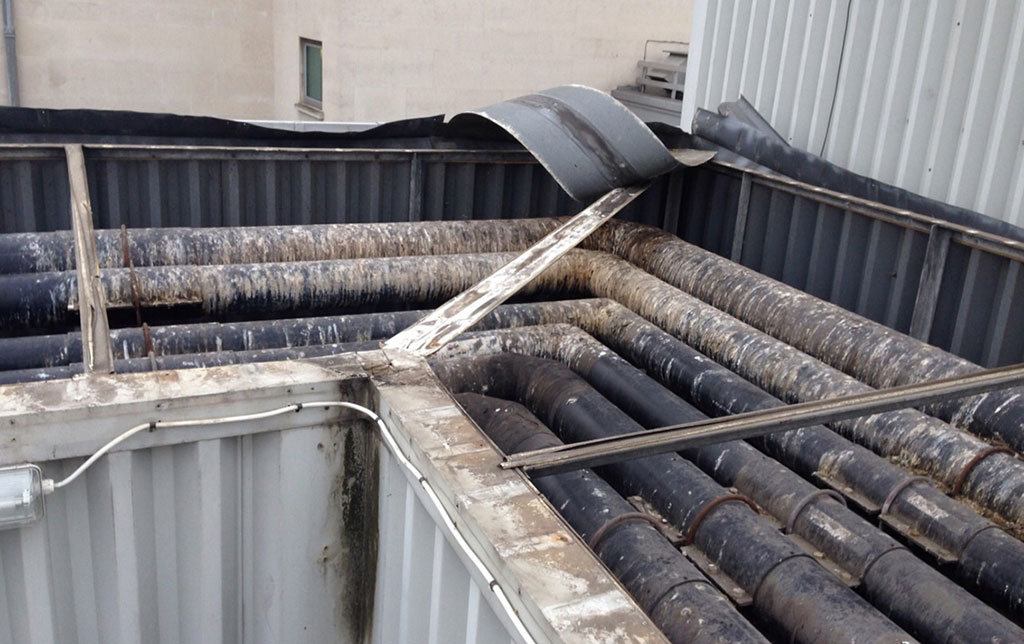
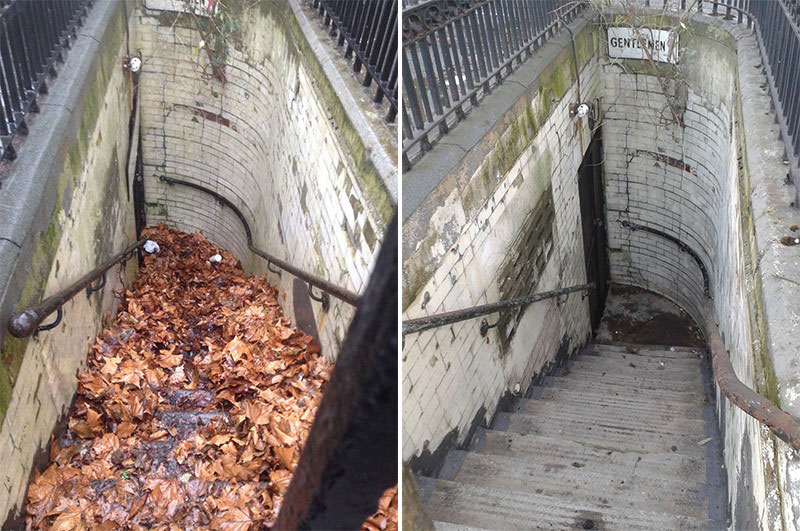
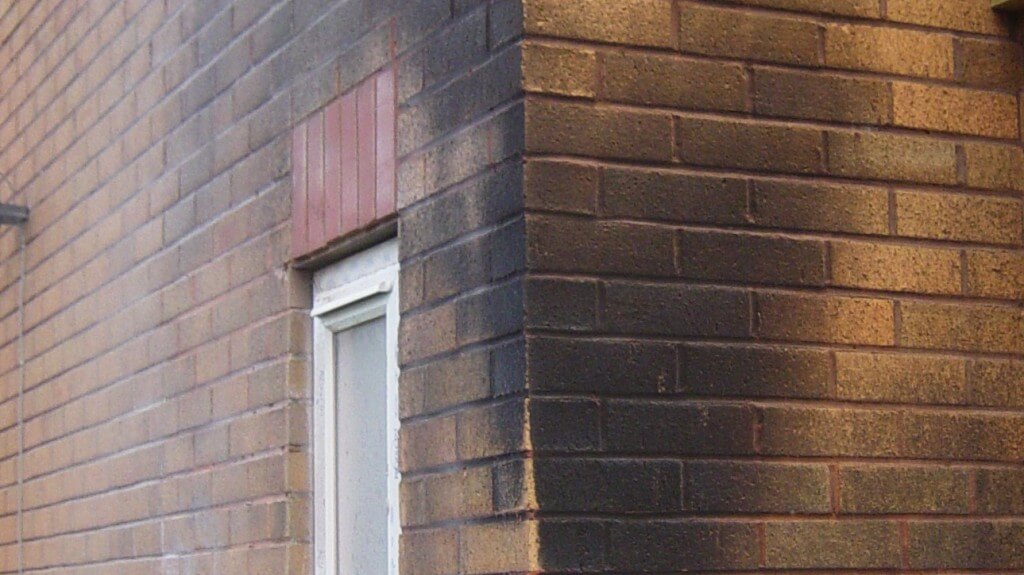
Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death should a fire break out in-doors. It contains chemical compounds and poisonous gases which can linger is smoke damage is not dealt with. Similarly, soot is equally as dangerous for your health because it enters and settles deep into your lungs causing serious health issues.
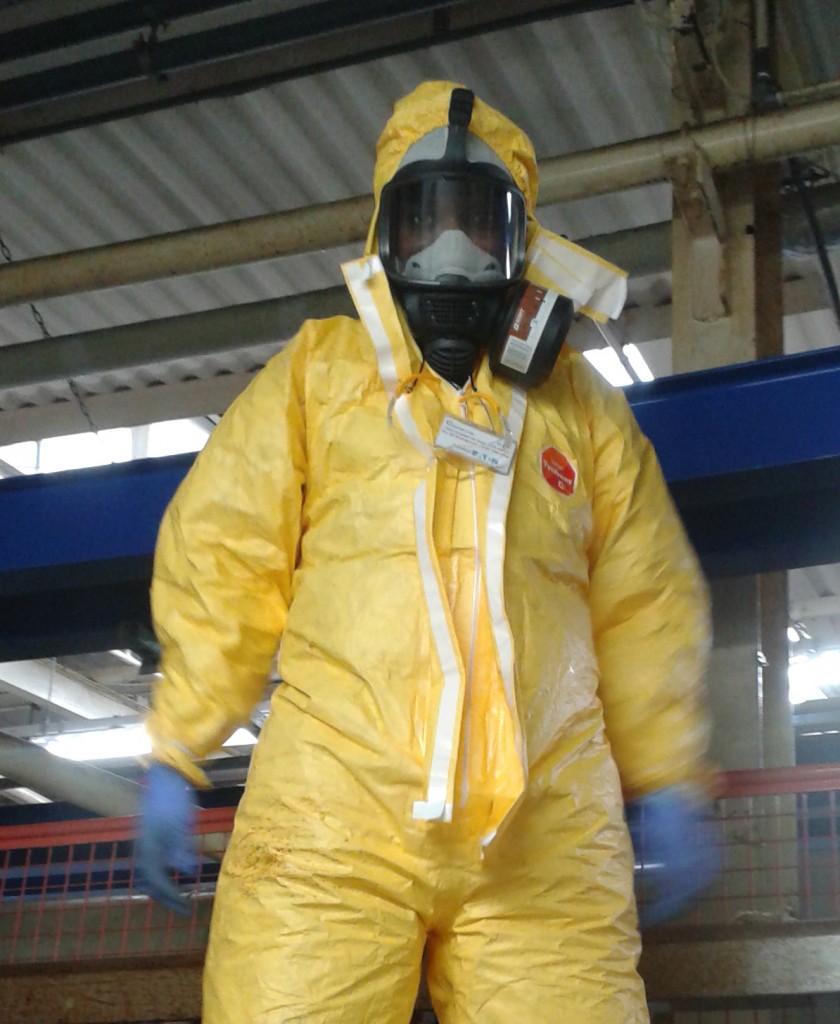
Heat Damage – This is thermal damage to the body’s tissues. The respiratory tract is especially vulnerable if you inhale smoke or soot at high air temperatures. Heat damage can occur to the mucus linings of the nose and mouth if you are unprotected.
Asphyxiation – Most health damage and deaths result from inhalation of toxic smoke. The smoke may physically block the fine airways in the lungs. If this smoke is especially toxic, it will reduce the blood’s ability to deliver oxygen to the body’s tissues and organs. This may result in organ damage or failure, unconsciousness and/or death.
Lung irritation – smoke and soot particles are so tiny and may contain toxic chemicals even after the fire has been extinguished.
Smoke particles contain many chemicals and even being in a room after the fire has been extinguished without respiratory protection, can result in these particles getting into the lungs causing irritation.
If you suffer from coughing, shortness of breath, sore throat, headaches or confusion following inhalation of smoke contact you doctor immediately.